Where is the global market of polyethylene films heading?
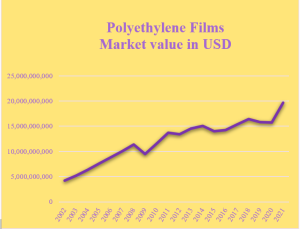
The last 20-year trend of dollar value changes for international exchanges related to products under the 392010 HS code. (Reference: www.comtrade.un.org)
We can easily find out by taking a look at the above chart that international trade, and naturally the consumption of goods under the 392010 hs code, has almost always been increasing in a way that the global market value of this group of goods during the last 20 years has raised to nearly 4.7 times; from 4.2 B USD in 2002 to 19.7 B USD in 2021. Therefore, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of this product group’s international exchanges has been at around 5%, which was slightly higher for the stretch film at about 6%. It is expected that the international trade and use of polyethylene films grow at an even faster rate in the next 5 to 10 years.
If you are asking why and on what basis?,
You’ll probably find your answers by reading the rest of this article:
What goods are classified under the 392010 HS code?
Where do we use these goods?


Plates, sheets, films, foils, and strips of non-cellular ethylene polymers are all subcategories of the 392010 hs code. Of course, stretch film and shrink film are among the most important and widely used products of this group. Most manufacturers have benefited from these films because of being well cost-effective, easy, flexible, and fast to wrap for packaging all types of primary, secondary, and, if necessary, tertiary packaging. Today, it’s very routine to use stretch or shrink films, and it doesn’t matter if you sell wholesale or retail; you can use his type of packaging for all audiences.
Why do we widely use stretch film in packaging?

The extraordinary privileges of these films in the packaging such as being fast, flexible, hygienic, and cost-effective along with the change in customers’ taste towards daily consumption of fresh and ready-to-eat products are primary reasons why polyethylene films are getting more and more popular among both producers and consumers. In addition to all these factors, in line with the world population increase in the third millennium, the value of global GDP has constantly been growing in the last 20 years and has reached from about 33 T USD to about 85 T USD. Naturally proportional to this production growth, the need to pack manufactured items has also increased and it seems perfectly reasonable to consider a direct correlation between the global GDP and the consumption of polyethylene films in packaging.
In the chart below, you can see the growth trend of the World GDP since the beginning of the third millennium. With a simple visual comparison with the chart of polyethylene film exchanges, you can see that there is an incredible harmony between the global GDP increase and the growth in the trade of polyethylene films; an upward trend that will continue according to the prediction of growth in the world’s population in the coming years.
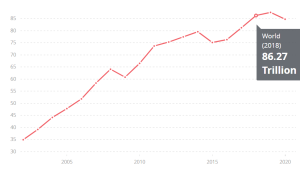
The trend of changes in the value of global GDP / Reference: World Bank (www.data.worldbank.org)
During the first 20 years of the 21st century, except for a few declines in line with the global production decrease in 2009 or 2015 due to the massive economic recessions and 2020 due to the Corona pandemic crisis, the exchange value of these materials has always been on an increasing trend. Considering this model, we can logically expect growth in the exchange and the consumption of these materials; that’s because anticipations about global GDP in 10-to-30-year horizons indicate a doubling of production. Moreover, we expect that in the coming years, due to the health sensitivities of the post-corona era, final consumers will care more about sanitary packaging; consequently, manufacturers will face tighter competition and try to consider this concern of customers by applying more of these films.
How are the demand trends of stretch film evolving?

Stretch pallet, with a share of about 60%, has the largest consumption share among other applications of stretch film, but the demand for the food-grade stretch film is growing at a faster rate and will have a larger share of this market in the future. On the other hand, we see an increase in demand for 5-layer stretch films, which are quickly replacing 1- and 3-layer films; these 5-layer films are thinner but more resistant simultaneously. Therefore, by consuming a smaller volume of these materials, we can achieve a more optimal result in favor of both clients and nature.
Shrink label; the popular packaging method for plastic- or glass-bottle products

The demand for shrink labels continues to increase rapidly. Being mainly produced based on PVC, and being flexible, transparent, anti-scratch, and printable via various methods, especially flexo printing, shrink label has created many possibilities for attractive introduction and promotion of products. Besides PVC, the material used to produce shrink labels can be also based on other materials such as PETG, OPP, PLA, or EPS. The labels produced from polyolefin, being more easily recyclable and more nature-friendly are in more demand than PVC.
Stretch hood film; a newer method for more optimal packaging

Stretch hood films are packaging films produced in various sizes according to the dimensions of pallets and cover them from above like a bag. The most important advantages of this packaging method are higher throughput, better transparency of the barcode for scanning, and the ability to unify and integrate the load on the pallet. We need to consider the use of this method requires hooding pallet machines. Although these machines still do not exist in most factories, the demand for these hooding films has been growing surprisingly, which reflects their massive potential in the future and their popularity among manufacturers.
Sources and references:
All the numbers and figures mentioned in this article are taken from the websites of the World Bank, the United Nations Trade Information Bank, and trademap.com.






